Reducing Rice Straw Burning and Harvest Losses in the Philippines
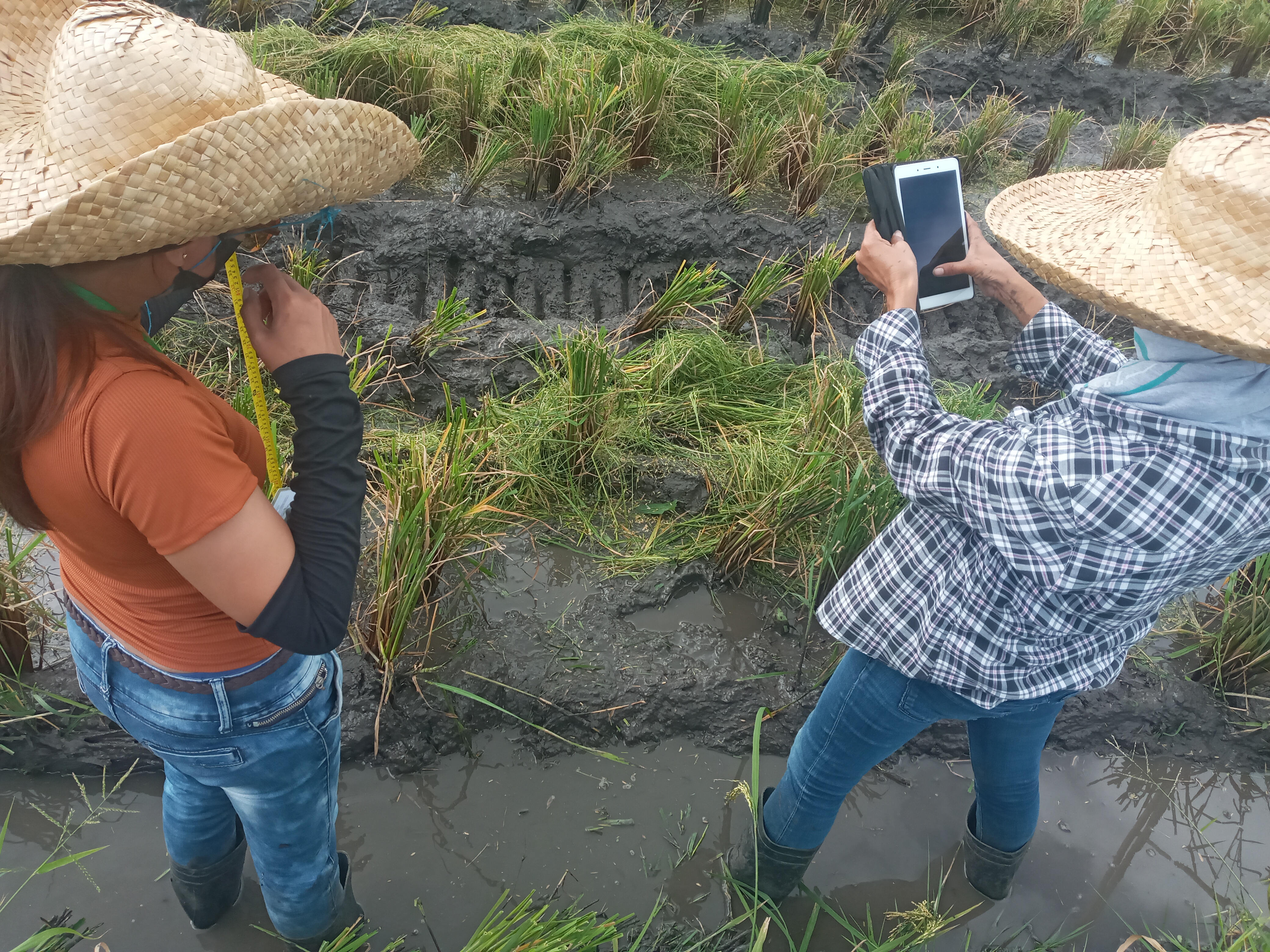

In collaboration with IPA Philippines and Straw Innovations Ltd., researchers are conducting a randomized pilot evaluation to measure whether a rice harvesting technology that removes rice straw directly from fields reduces straw burning and grain loss and improves yields.
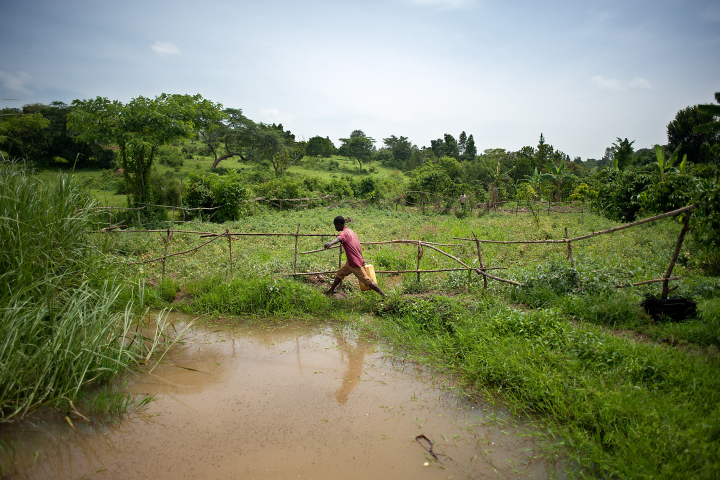
The Philippines is the eighth largest rice producer in the world, and the rice industry accounts for the livelihood of more than two million households in the country.1 However, a significant challenge of rice farming is post-harvest straw management. Straw is typically burned in the field, emitting greenhouse gasses and causing serious health issues like asthma and pneumonia.2 Additionally, poor harvesting technology can lead to up to 20 percent of rice being lost.3 To eliminate straw burning, its associated environmental impacts, and reduce harvest loss, Straw Innovations Ltd.—a provider of a new rice harvesting service—developed a harvesting technology that removes rice straw directly from fields.
In collaboration with IPA Philippines and Straw Innovations, researchers are conducting a randomized pilot evaluation to measure farmers’ willingness to adopt the new rice harvest technology and its impact on farmers’ rice yields, grain losses, and rice straw management. For the 2023 wet season harvest, rice farmers were randomly assigned to either receive a discounted offer of Straw Innovations’ services or continue with their existing harvesting service and serve as a comparison group.
During the 2024 dry season, researchers conducted a willingness-to-pay (WTP) exercise with a randomly selected group of farmers, and farmers were offered discounted rice harvesting services by Straw Innovations accordingly. Rice farmers were also surveyed to gather harvesting details for both the 2023 wet season, and the 2024 dry season. In addition, researchers approached a subset of farmers in these seasons to gather actual field measurements on rice grain losses, moisture content, rice yield, and GPS tracking of rice fields at harvest.
Results will be available later in 2024.
Sources
1. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Economic Research Service, “Rice Sector at a Glance,” https://www.ers.usda.gov/topics/crops/rice/rice-sector-at-a-glance/;
Philippines Department of Agriculture, Philippine Rice Research Institute, “The Rice Data Analytics Dashboard,” www.philrice.gov.ph/ricelytics/profilemain. Accessed September 27, 2024.
2. AMK, El Safty. "Environmental and health impact of open burning rice straw." Egyptian Journal of Occupational Medicine 44, no. 3 (2020): 679-708.
3. Julien Claes, Djavan De Clercq, Nicolas Denis, David Fiocco, and Joshua Katz, “How to reduce postharvest crop losses in the agricultural supply chain,” McKinsey & Company, November 18, 2021, https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/agriculture/our-insights/how-to-reduce-postharvest-crop-losses-in-the-agricultural-supply-chain
Implementing Partner

Funding Partner