Improving Financial Behavior with a Tablet-Based App
Abstract
The social enterprise Fundación Capital is scaling up an initiative that lets low-income people learn financial concepts at their own pace, from anywhere.
In an evaluation by an IPA research team, researchers found the program improved financial behavior. As of September 2019, Fundación Capital had expanded the initiative to reach approximately 520,000 individuals in Brazil, Colombia, the Dominican Republic, Honduras, and Mexico. Over half of this expansion was supported by the USAID-Skoll Innovation Investment Alliance, which made evidence of impact one of the conditions for funding.
The Challenge
People across the world are susceptible to making faulty financial choices, which can impact their long-term well-being, especially for the poor who have little margin for error. Lack of knowledge is considered a major reason why people fail to make sound financial decisions. While financial education classes are a widely used tool to give people the knowledge and skills for making sound financial choices, a large body of evidence suggests that the conventional approach to financial education programs, which typically teaches financial concepts in classroom-style settings, is not only expensive at scale but also ineffective. Some evidence suggests that customizing financial education to the needs, interests, and location of each participant – and making it more entertaining – are more effective approaches, but finding a cost-effective and scalable way to implement customized training has been a challenge.
Fundación Capital, an international social enterprise dedicated to reducing poverty at scale through public and private sector partnerships, designed a new initiative with the goal of “freeing financial education.” Through the LISTA Initiative, community leaders facilitate access to the training app via shared tablets and smartphones, to achieve economies of scale. Participants are able to learn from the comfort of their own homes, study at their own pace, and customize their learning by focusing on topics most relevant to them. LISTA integrates audio, video, simulators, and gaming elements in an attempt to overcome literacy barriers and make the experience more entertaining.
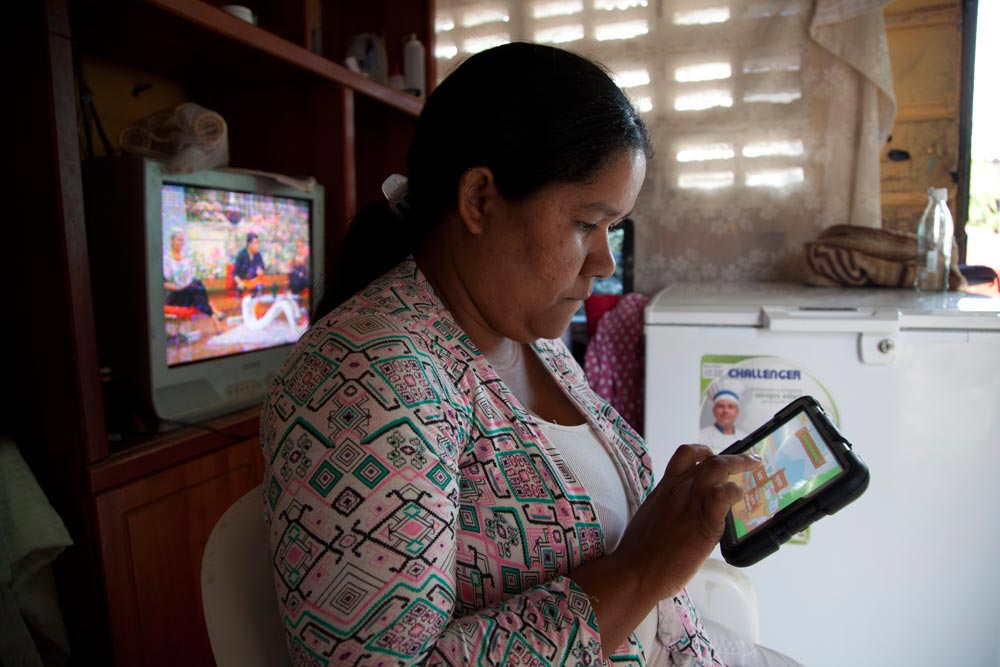

The Evidence
An IPA evaluation tested the impact of LISTA’s tablet-based application on financial knowledge and attitudes, informal and formal financial practices, and the use of financial products by participants of Colombia’s conditional cash transfer program (about 90 percent of whom are women). Results indicated that the LISTA tablet initiative had significant impacts on financial knowledge, attitudes toward formal financial services, adoption of financial practices, and financial outcomes. Women who used the LISTA app had a better understanding of savings and budgeting concepts, expressed increased preferences for saving formally rather than informally than women who didn’t have access to the tablets. In general, impact increased the poorer, the less educated, and the more rural the population.
Importantly, LISTA participants demonstrated a greater ability to put their knowledge into practice than those in the comparison group, as they were more likely to set savings goals. These women also reported saving more informally immediately after receiving the tablet and had higher account balances (according to bank data). Two years after the program started, they continued to report increased informal savings and had less debt in the formal credit sector.
The Impact
These results contributed to Fundación Capital's scale-up of the LISTA Initiative. Existence of evidence of impact was one of the conditions for funding from the USAID-Skoll Innovation Investment Alliance. Lead researcher Matthew Bird shared the results with the funders, informing their decision to support the expansion. This support helped reach an additional 268,000 individuals in Colombia, the Dominican Republic, Honduras, and Mexico, with over 520,000 users overall in eight countries by September 2019.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.